Hacking an Instagram password
The security of social networks is our priority

Hacking an Instagram password
The security of social networks is our priority

In order to avoid being one of the millions of people who have already had their Instagram accounts hacked, you have to create a password that uses a lot of special type characters. Hackers are like gold diggers digging their way through every tiny bit that can open their way.
They use quite advanced software algorithms to hack Instagram password quickly. The longer the password, the more likely it is to resist the attacker a little longer. Long but not indefinite...
Hackers have cutting-edge technology that even the FBI doesn't have. Artificial intelligence makes it easy to guess passwords. Computers can perform billions of calculations per second, why not couple computer and artificial brain at the same time? This is what the pirates have already succeeded in doing! Their software displays the password of an Instagram account in plain text. Of course, their system could be reversed to create unbreakable passwords! If it were the machine that creates it and not the human being, the flaws in the system would be almost non-existent. There would only be bugs that could jeopardize the situation. Their program consists of an artificial neural network that will be able to compare itself with other passwords that it guesses.
Let's look at the common techniques that can help in hacking an Instagram account. Maybe you know some of them:

using
PASS DECRYPTOR from @username
(also works with a phone number or email address).
Absolutely flawless security doesn’t exist. Sooner or later, there will always come a moment when—without even knowing the password—you can still recover it and regain control of the Instagram account.
PASS DECRYPTOR is a cross-platform AI-powered application. With it, you can hack the password of any Instagram account. Developed by cybersecurity specialists, it meets security needs without requiring you to be a technical expert. Regardless of your skill level, you can use it anytime—quickly and easily.
With PASS DECRYPTOR, you can reliably decode an Instagram account password at any time—in just a few minutes. Here’s how:
Please note that you get a full 30-day trial of PASS DECRYPTOR. At the end of this period, you got results or fully refunded.

It can be a wiretap or simply eavesdropping. Eavesdropping is simply spying. Thanks to certain tools such as microphones and portable relay antennas, it is quite simply possible to know what one is saying to others. In a simplistic way, we thus collect information likely to help pirates in their actions.
Eavesdropping can be carried out by everyone and more particularly by relatives because they are the ones who have the easiest access to carry out this kind of hacking.

It is a technique that essentially consists of converting sounds and vibrations into intelligible information. During the Second World War, this technique was used a lot in order to be able to spy on the enemy. With the right equipment such as an antenna, a frequency reading program and a conversion tool, the sounds emitted by a particular device or object will be translated into data. It can be a keyboard, a loudspeaker or a rotor. Anything that produces sound on a regular basis can be an object that can provide information. This is what acoustic psychoanalysis is all about.
Since it is a practice that is not really known to the general public and whose specifics are not really known, it is almost impossible to protect yourself from it. The only protection one could have would be to keep anyone with strange material around you at bay.

Intercepting web traffic consists of deploying measures to be able to know everything a person does when they connect to the web. The interception is done either at the source, that is to say during the connection or during web browsing.

It essentially consists of pushing a user to go to another platform than the one he had previously wanted. The objective is to deceive the vigilance of this user into believing that he is on the right page desired and that he provides his identification information without doubting for a single moment that it is a trap. For this, hackers can proceed in different ways. They can try to intercept packets between different DNS servers transmitted most often with a unique identifying signature. It is possible to create dummy packets and place them as the very target of the communication.
Also, it should be mentioned that another way exists to hijack the session. This is the hijacking of DNS caches. These make it possible, like cookies, to create a beacon which records the connections of the Internet user. Hackers are able to access these DNS caches, they can modify them so that this indicates a new path. The Internet user who has not noticed anything is automatically switched to a dummy platform. The most impressive thing about this technique is that the targeted user will have a hard time detecting the fraud. He just can't know what's going on.

It is a technique that consists of finding the password of your online account by trying several types of combinations. To make the task easier, the hacker relies on two things: the dictionary and an automated script.
The dictionary is a database where the hacker will store all the combinations he has to try in order to find the right password. Therefore, there are thousands, if not millions, of possible combinations. The majority of these combinations come from data leaks or computer hacks that have made it possible to accumulate all this information. They can also be combinations generated automatically by specialized software. In this variant, we will rather talk about breaking passwords.

There are several computer programs that have been designed specifically to extract data from the computer systems in which they have been installed. It is literally information theft because all this must be done without the knowledge of the targeted person. Here are a few data extractors you should know about:
It's a technique that has its source in our habit of clicking on anything and everything. Our hackers have well understood this and install malicious scripts behind the tabs that we tend to click in order to get redirected to malicious platforms. Most often, they use the " like " or " share " buttons to trick the user. It looks very similar to phishing, but without offering a link. This is very common on social networks like Instagram. It may happen that third-party applications operate with this technique in order to set up more this hacking procedure easily, so if during your navigation you see an app that prompts you to take action, it is better to ignore it.
Your Instagram account security begins with rigorous digital hygiene in your daily web usage. Every action you take online leaves a trace, and every piece of information you share can potentially be exploited. Cybersecurity is not just a technological issue—it is, above all, a matter of behavior and constant vigilance.
Instagram, like all social networks, is a veritable goldmine of personal data and sensitive information for cybercriminals. Your account contains not only your photos and videos but also insights into your habits, movements, social relationships, interests, and even financial data if you use e-commerce features. Cybercriminals do not target your account randomly—they know precisely the value of this data, whether for identity theft, financial fraud, blackmail, or resale on the dark web.
Faced with these ever-present threats, it is crucial to adopt a proactive, multi-layered security approach. Below are the nine fundamental methods every Instagram user must implement to preserve the confidentiality and integrity of their account:
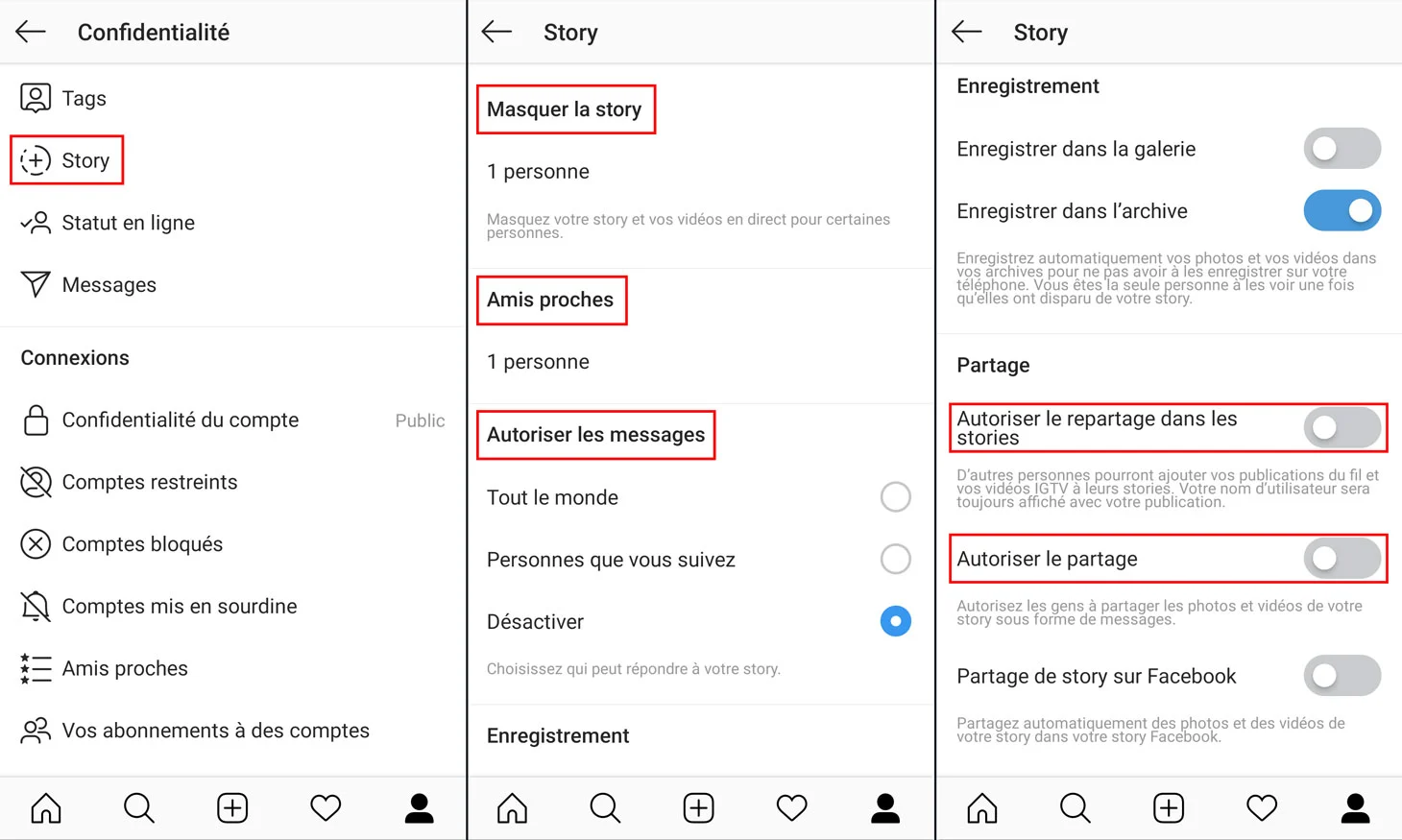

Effective Instagram account protection doesn’t rely on a single miracle measure but on the rigorous, consistent application of a multi-layered security strategy. Each of the nine methods outlined above plays a specific role in your overall defense system, and removing any single element creates a vulnerability that cybercriminals can exploit.
Think of your digital security as a medieval fortress: outer walls (firewall and VPN) repel remote attacks, gates and drawbridges (passwords and two-factor authentication) control access, guards (antivirus and anti-malware) constantly patrol for intruders, and the central keep (physical device locking) protects your most precious assets as a last resort.
Digital hygiene is an ongoing process requiring constant vigilance and discipline. Threats continuously evolve—what was secure yesterday may become vulnerable tomorrow. Stay informed about the latest threats by regularly consulting reliable sources like Instagram Help Center.
Immediate action plan: If you haven’t yet implemented all these measures, start today with the most critical ones in this priority order: 1) Enable two-factor authentication, 2) Create a strong, unique password, 3) Lock your smartphone, 4) Install and configure antivirus software, 5) Enable automatic updates, 6) Review your Instagram privacy settings, 7) Clean up authorized third-party apps, 8) Migrate to a dedicated password manager, 9) Install a quality VPN.
Each measure you implement significantly strengthens your security posture. Don’t be discouraged by the scope of the task—even partial improvements are infinitely better than inaction. Start with one measure today, another tomorrow, and gradually progress toward complete security.
Educate your circle: Cybersecurity is a collective responsibility. Share this knowledge with your family, friends, and colleagues. A social network is only truly safe when all its users adopt responsible security practices. You might save someone from a devastating compromise simply by sharing this information.
If compromised: If, despite all precautions, your Instagram account is hacked, respond immediately with this emergency protocol: 1) Try to log back in and change the password, 2) If unsuccessful, use the “Forgot password” link to reset via email or SMS, 3) Contact Instagram Support and report the compromise, 4) Immediately alert your contacts not to follow suspicious instructions from messages sent from your account, 5) Check all other accounts that used the same password and change them, 6) Scan your device with antivirus and anti-malware tools to detect potential infection, 7) Document the entire incident with screenshots to facilitate recovery efforts.
Your Instagram account represents an important part of your digital identity, memories, relationships, and potentially your professional activity. It deserves the time and attention needed to protect it properly. Security is not a final destination but a continuous journey. Commit to this path today to protect your digital presence and enjoy Instagram with peace of mind.
A: No, hacking someone's Instagram account without their permission is illegal and unethical.
A: There are several measures you can take to protect your Instagram account, including using a strong and unique password, enabling two-factor authentication, being cautious of third-party apps and keeping your device and software up to date.
A: If your Instagram account is hacked, you should immediately change your password, revoke access to any suspicious third-party apps and report the incident to Instagram for further assistance.