Hack a Facebook account
Have instant access
to any Facebook profile

Hack a Facebook account
Have instant access
to any Facebook profile

We are going to explain to you the different methods on Facebook hacking. Security is the priority of users, Facebook does enough communication on it. Protect your profile and your friends who could be contaminated later by a hacker. You should read the techniques very carefully, watch out for attacks and protect your Facebook account from hackers.
Again, everything we are going to reveal here is only to be used to learn how to protect and educate yourself. Do not use these methods to do illegal things. Don't do to others what you don't want them to do to you!
To hack a Facebook password, some hackers push the limits of their imagination very far. Do you know the methods used by hackers to hack a Facebook? You should know first of all that hacking techniques evolve according to the context. Indeed, the method that may be suitable for a hacker will depend on the security you have deployed around your account. Here are some techniques that you absolutely must master if you hope to protect yourself against this cyber attack.

using PASS FINDER and @username
(also works with a phone number or email address).
Regain access to a Facebook account easily with PASS FINDER. This application was developed by cybersecurity experts so that anyone can use it. Its simple and intuitive interface allows you to recover a password using an email address, a @username, or a phone number.
Once you’ve entered the account details in the appropriate field, click the “OK” button and let the software find the Facebook account password for you.
Take advantage of this solution! You can try it right now by downloading it from its official website: https://www.passwordrevelator.net/en/passfinder
With the 30-day trial offer, you can ask for refund.

Identity theft can be a violation of the integrity of your Facebook account. By speaking of identity theft, we are more referring to account theft when the cybercriminal creates another account with your photo and maybe even your name while trying to impersonate you. Of course, this can trick your loved ones and anyone you don't really have immediate contact with into verifying your identity.

What is session hijacking and how does it affect Facebook account security? Hijacking a session consists in directing a user of the Internet network or of a web service to another platform than the one to which he would like to access the database. Obviously, the diversion is made so that the target of this attack does not realize the subterfuge. To achieve this, cybercriminals can use several methods:
The DNS (for " Domain Name System") is a computer service that is mainly used to redirect internet domain names, IP addresses or any type of record to identify an official platform. In other words, this service is more than essential for the proper functioning of the web as well as all affiliated platforms. However, its usefulness is such that if cyber criminals manage to gain access to it, they can create devious paths which are likely to trick users into getting to their usual platform. For example, if one or more of the DNSs that allow communication between a platform (browser) and Facebook have been poisoned (i.e. cybercriminals have managed to inject malicious code into the cookies stored by these DNSs), when'facebook.com ”, it is not to the official Facebook website that it will be directed but rather to another dummy platform which takes up the colors and codes of Facebook. The user who will not have realized anything, will enter his login credentials and will be hacked. The hackers will recover these identifiers and then use them. It is true that this technique strongly resembles phishing. However, a very important difference must be exposed: in the hijacking of sessions by DNS poisoning, the victim does not need to click on any link. Everything happens from the base, from its browser. And the worst is when the poisoning goes back from the DNS of the internet service provider, the victims have no way to defend themselves against it.
Cookies are another way to hijack a user's session. If this strongly resembles the first one that we have just described, it should nevertheless be mentioned that it draws its source from the cookies most often saved during our visits to websites. One of the functions of cookies is to create a much easier path which makes access to a website faster. When you store cookies from Facebook websites, for example, accessing your Facebook account from the same browser will take less time than the first time. In other words, cookies will serve as a kind of beacon that will mark your connection to the website in question. When hackers manage to retrieve these cookies, they can hijack the path you have already made every time you log in. Therefore, when you try to go to "facebook.com ”, the connection will be diverted and you will be in the same case as the one mentioned above.
This is obviously a very complicated technique and reserved for hacking professionals. It is a method that uses security vulnerabilitiespresent in the mode of packet transmission between DNS servers. Indeed, the servers in question tend to communicate using unsigned packets and they are generally authenticated with unique request numbers. This means that it is possible for the hacker to discover request numbers and create new ones. Thanks to this, it is easy for him to be able to intercept connections. Of course, if he succeeds in this, he can either redirect the Internet user to a phishing website or simply collect this personal data without his knowledge. If two people are on the same network for example and one of them wants to connect to Facebook, the second can very well usurp the login page where you enter your Facebook identifiers and password by replacing it with a fake page that you will have created from scratch! The trick is played on the DNS address which was previously changed and replaced by a fake one. The end user will not see anything at all and will think they are on the original Facebook page. This hack is often used when connecting to the Internet in public places. When a person connects to the Internet, there is a 90% chance that they want to access their favorite social network.
It is a method that will consist for a hacker to take the time to get to know his victim better. In this process, he gradually collects information that he can later convert into login data. He will first try to establish a link between him and his victim and then analyze all of his activities, whether in real life or digitally. The practice is almost like social engineering. However, spidering requires much more attention and applications than the latter. Of course it is much more efficient. To facilitate the implementation of this rather delicate attack, the hacker will use automated software that will allow him to analyze all the information they have collected. The goal is to find login credentials through these searches.
Spearphishing is a dangerous and more applied variant than phishing. It is mainly used to target a specific person. If the overall process remains the same, this method will consist of sending a message that contains a link. The link on which the victim must click to be redirected to a platform where their login credentials will be stolen. However, in the current context, before sending a message, the hacker will find out about his victim. It will collect enough information in order to compose a message that will be infallible. The idea is, for example, to usurp the identity of a relative, or to usurp that of a website where the latter usually goes there. The message will consist of information that makes the target feel confident. And when the goal is reached, he is automatically trapped and his connection data is collected. This is where the main danger lies. This practice is quite facilitated by social networks where it is often possible to have a lot of personal information on potential targets.
This is clearly a must when talking about Facebook hacking.
Facebook is a social network where several people meet to exchange and build relationships. This is why social engineering is a very common factor on Meta's social network. Social engineering is manipulation, it is not strictly speaking hacking. It generally consists of taking advantage of a link with its target to collect essential information. In other words, if you are targeted by social engineering, it is necessarily with a person who is used to interacting with you, either a friend or a close family member. It is for this reason that when you are on Facebook, it is not necessary to answer all the questions. You should also be careful when commenting on the posts of your friends or unknown. Thanks to your comments, hackers can simply try to do an analysis to determine your passwords. For example, avoid answering this type of question:
More often than not, social engineering, when applied in a general way, essentially uses this kind of question that the victim has provided themselves.

It is a technique that uses automated software to find your password by making hundreds or even millions of combinations of letters, symbols and numbers. And this in specific situations. Password cracking is regular. It is common for hackers to use it. This is why it is important to take care of your password. The software used in this context is sophisticated.

When it comes to data leakage, Facebook is one of the platforms that are most affected. A data leak most often occurs for various reasons. Either for configuration errors, server failures or because of computer hacking. Every year, the parent company behind Facebook, Meta, is implicated in some way with a data breach. We usually talk about this when the platform that is concerned leaks personal, professional or sensitive data out of its surveillance, allowing anyone to be able to access it in different ways.
In the event of a data leak, there are certainly great risks that your personal data has been compromised. This may involve your login credentials. If a hacker manages to get his hands on a database, he could easily initiate the dictionary attack. The dictionary attack is a technique which consists for a hacker, to use an automated script in order to find a particular password by using as a reference a database where he could compile passwords potentials.

Securing your Facebook account requires proactive measures against evolving cyber threats. With billions of users, Facebook remains a prime target for identity theft, phishing attacks, and data breaches. This comprehensive security guide outlines essential steps to protect your personal information and prevent unauthorized access to your Facebook account.
Facebook account security relies on implementing multiple protective layers. While perfect security doesn't exist, following these proven measures significantly reduces your risk of compromise. Proactive protection is far more effective than attempting recovery after a breach occurs.
Key Security Risks for Facebook Users:
Implement these seven essential security measures to create a robust defense system for your Facebook account.

A: No, hacking into someone's Facebook account without their permission is illegal and unethical.
A: No, the methods provided in this article are for educational purposes only. Using them for illegal activities is prohibited.
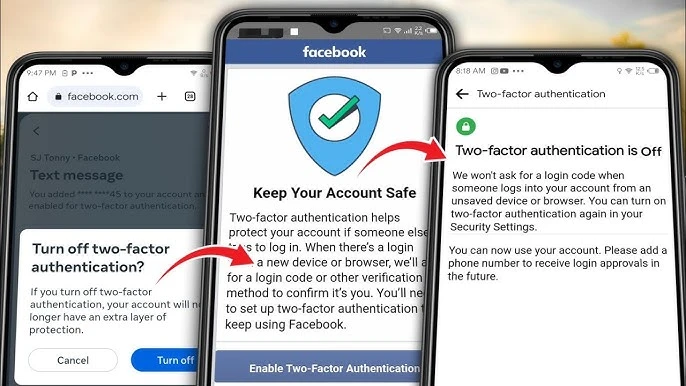
A: There are several steps you can take to enhance the security of your Facebook account, including enabling two-factor authentication, using unique and strong passwords, being cautious of third-party apps, keeping your devices and software updated, avoiding public computers and insecure WiFi networks and securing your device with a password or biometric measures.
A: If you believe your Facebook account has been compromised, you should immediately change your password, review your account activity for any unauthorized actions, revoke access to any third-party apps you don't recognize and report any suspicious activity to Facebook.
A: No, there is no guaranteed method to hack into someone's Facebook account. Additionally, attempting to do so is illegal and unethical.